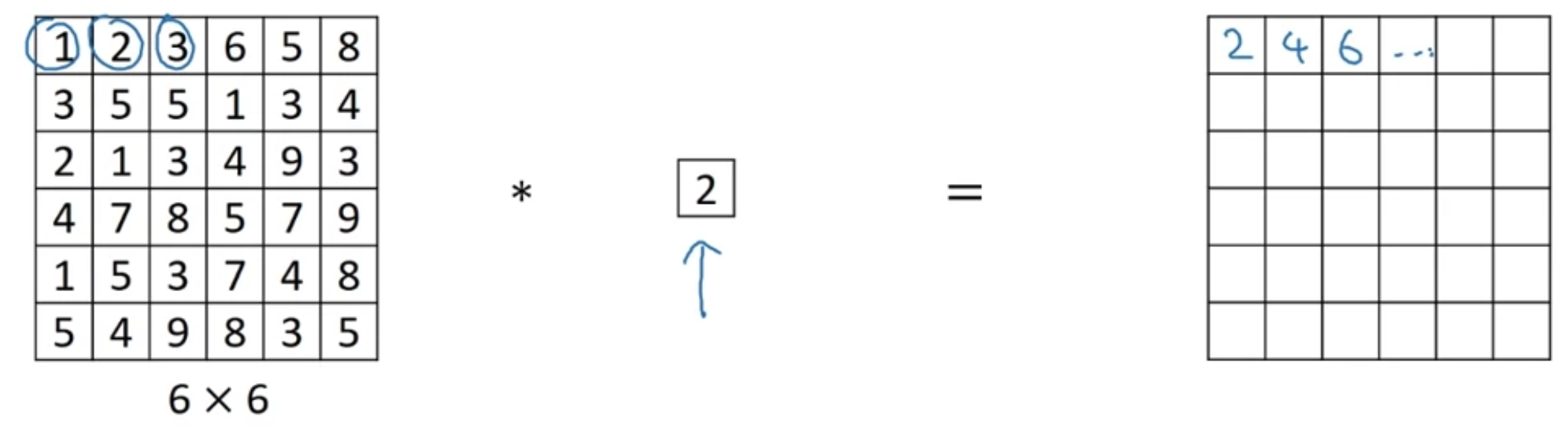
Networks in Networks and 1x1 Convolutions
[1x1 Convolutions]
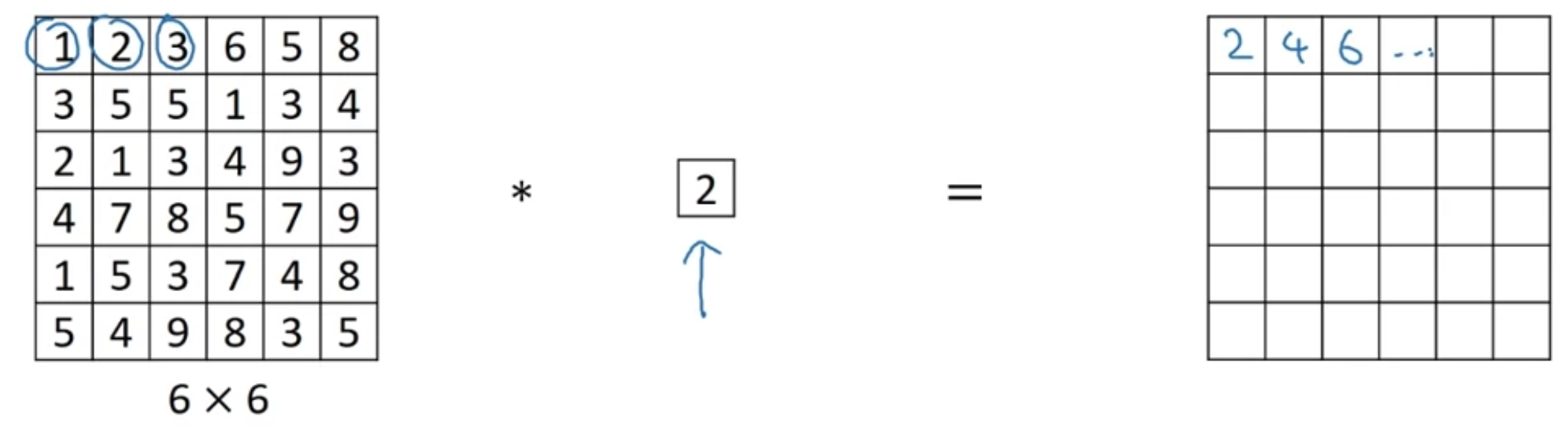
여기서는 그냥 2배 곱하는 효과밖에 안 됨 (input이 6x6x1 이미지)

하지만 채널수가 32개라면 어떨까? 1x1 블록은 volume(channel)을 가로질러(-> one slice) 한 위치의 픽셀값들을 확인할 수 있게 해준다
마치 32개의 입력값을 받는 신경망 노드 하나의 역할을 하는 것이다 + 1x1블록 filter가 여러개라면 여러 노드를 이루는 것
"It is basically having a fully connected neural network"
"one-by-one convolution" 혹은 "network in network"라고 부름
[Using 1x1 convolutions]

height/width는 괜찮은데 채널수는 너무 커져버렸다! 크기는 유지하고 채널수를 줄이는 방법은?
--> 1x1 conv filter를 32개 사용한다
- 각 필터는 $(1, 1, 192)$ 차원
--> 만약 filter 192개를 사용하면? output은 28x28x192가 되고, non-linearity를 통과한 효과가 있을 것임
cf) Pooling layer는 h, w 를 줄이는 데 사용되었었음
Inception Network Motivation
Inception: conv 쓸까? 필터 크기는? 풀링은? --> "그런 거 고민하지 마, 그냥 다 해."

28x28x192 볼륨이 입력되었다고 하자
처음에는 1x1 사이즈의 필터 64개를 적용하여 output volume을 받는다
그 다음 3x3 사이즈의 필터 128개를 적용하여 받은 output volume을 그 위에 쌓는다
그 다음 5x5 사이즈의 필터 32개를 적용하여 받은 output volume을 그 위에 쌓는다
그 다음 Max-Pooling 필터 32개 사용하여 받은 ouput volume을 그 위에 쌓는다 (concatenate)
총 256개 채널을 가지게 됨 -> 28x28x256
- volume들을 쌓기 위해서는 같은 크기로 유지해야 한다
- 같은 크기로 유지하기 위해 max pooling 적용시 특별히 same padding, stride=1 을 사용한다
문제는 computational cost

위 예시에서 5x5 conv 적용하는 부분만 가져와봄
각 필터 크기는 5x5x192
그렇게 됐을 때 계산량 : $5 \times 5 \times 192 \times 28 \times 28\times 32$, 즉 120M
하지만 여기에 1x1 conv를 적용한다면?

1x1 conv 활용해서 확 줄어든 intermediate volume을 생성(채널수가 16) --> "bottleneck layer"
계산량 :
- 첫번째 conv $28 \times 28 \times 16 \times 192$ = 2.4M
- 두번째 conv $28 \times 28\times 32 \times 5\times 5\times 16$ = 10.0M
총 12.4M
(10분의 1로 줄어든 모습)
Inception Network

- 1x1 conv 먼저 연산하는 이유는 바로 위에서 설명되었음
- max pooling의 경우 채널수가 유지되므로, 채널수를 줄이기 위해 pooling layer 다음으로 1x1 conv 연산 실행 - 32 채널로 감소
- 마지막으로 channel concat
--> one inception module

inception block 들을 쌓아서 만듦

side branches: FC + softmax output
- 중간 레이어에서도 예측값이 나쁘지 않다는 것을 확인하고, regularize하는 효과를 줌
MobileNet
- 모바일환경에서 구동시킬 수 있을 정도로 가벼움


일반적인 convolution 연산에 드는 computational cost :
필터의 파라미터 개수 x 필터가 위치하는 개수 x 필터의 개수
$(3 \times 3 \times 3) \times(4 \times 4)\times 5 = 2160$
동일한 입력에 동일한 모양의 output을 출력하되, computational cost를 덜 쓰는 방법?
[Depthwise Seperable Convolution]

두 단계로 이루어짐 (depthwise + poinwise)
(1) depthwise convolution

채널별로 준비되어 있는 필터들을(필터개수x, 하나의 필터안에서) 입력 이미지의 각 채널에 적용한 다음에, 채널별로 output
-> 채널이 유지됨
-> computational cost
필터의 파라미터 개수 x 필터가 위치하는 개수 x 필터의 개수
$(3 \times 3 ) \times(4 \times 4)\times 3 = 432$
-> 여기까지 intermediate volume을 생성하였음
(2) pointwise convolution

맨 오른쪽의 output을 4x4x5 차원으로 만들고 싶다면
1x1x3 모양으로 된 filter를 5개($n_{C}'$) 사용하면 됨

input $n_{out} \times n_{out} \times n_{C}$ ---> output $n_{out} \times n_{out} \times n_{C}'$
-> computational cost
필터의 파라미터 개수 x 필터가 위치하는 개수 x 필터의 개수
$(1 \times 1 \times 3) \times(4 \times 4)\times 5 = 240$
[cost summary]
- normal convolution : 2160
- depthwise seperable convolution : 432(depthwise) + 240(pointwise) = 672
normal conv vs. depthwise seperable conv : computation cost의 비율
$$\frac{1}{n_{C}'}+\frac{1}{f^{2}}$$


MobileNet Architecture
less expensive한 depthwise seperable convolution 연산 사용

depthwise seperable convolution 블럭 13개 쌓고, 이어서 Pooling, FC, Softmax layer
[MobileNet v2]
1) residual connection 추가
2) expansion layer 추가

"bottleneck block"

- input을 residual connection 통해서 output으로 직접 전달
- non-residual connection(main) 에서는
- 먼저 expansion operator 적용
- 많은 양의 1x1x$n_{C}$ filter 를 적용한다
- depthwise convolution 연산 - 패딩 적용하여 차원 유지됨
- pointwise convolution 연산 - 1x1x$n_{C}$ filter 적용 (논문에서는 pointwise 대신에 projection 이라고 부름)
왜 bottleneck block이 필요한 걸까?
- expansion : bottleneck block 내부에서 representation의 크기를 키움 --> it enables a richer set of computations
- pointwise(projection) : 작은 크기의 값으로 다시 돌려놓음 --> keeping the memory
EfficientNet
How can you automatically scale up or down neural networks for a particular device?



baseline 신경망 구조가 있다고 하면 (1) 더 좋은 화질의 이미지를 활용하거나(resolution, $r$) (2) 신경망을 더 깊게 만들 거나(depth, $d$) (3) 더 넓게 만들 수 있다(width, $w$)
어떤 computational budget이 주어졌을 때, $r$, $d$, $w$를 어떻게 고르면 좋을까?

아니면 compound scaling - 동시에 여러개 scale up/down 하기
What's the best trade-off between r, d, and w, to scale up or down your neural network?
--> EfficientNet
'인공지능 > DLS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [4.3.] Detection Algorithms(1) (0) | 2022.07.28 |
|---|---|
| [4.2.] Practical Advice for Using ConvNets (0) | 2022.07.27 |
| [4.2.] Case Studies(1) (0) | 2022.07.24 |
| [4.1.] Convolutional Neural Networks(3) (0) | 2022.07.24 |
| [4.1.] Convolutional Neural Networks(2) (0) | 2022.07.24 |