Pinhole Camera Model
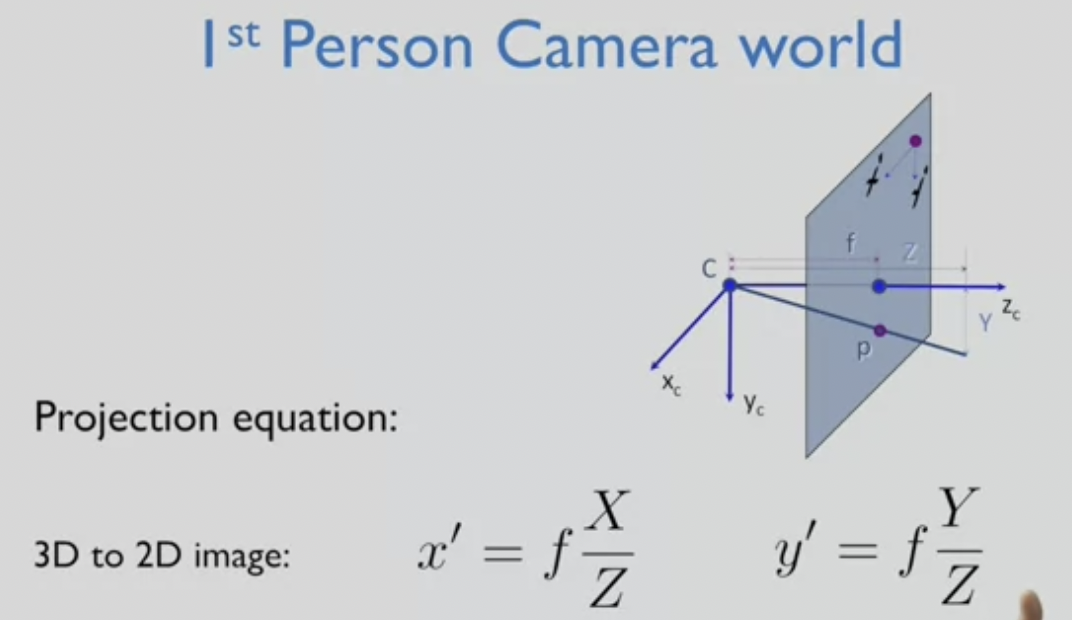
"First Person Camera World"
- 눈이 세계 정중앙에 위치한다고 가정
- (0, 0) 에 위치
- 모든 것은 나에 대해 상대적으로 측정됨
- 오른쪽이 x축, 아래가 y축, 오른손 엄지 세웠을 때 정면이 z축

- z축 방향으로 focal length(f) 만큼 떨어진 위치에 canvas를 둠
- 3D 세계에서 한 지점을 2D로 가져오려면 shrinking하게 되는데, 그것이 얼마나 멀리 있는지와 관련됨
- Z로 shrink하고 (멀어질수록 z가 커지므로, 멀리 있을수록 더 shrink하게 됨), f로 magnify함 (focal length 커질수록 더 magnify됨)
- image plane의 크기는 고정되어 있으므로, focal length 를 늘리면 field of view는 좁아지게 됨
중요한 질문들
1) where is the optical center of projection? where am i oriented?
2) how far is the focal length?
Focal Length and Dolly Zoom Effect
"focal length"
--> "zooming"
optical center와 focal length는 동시에 변화한다
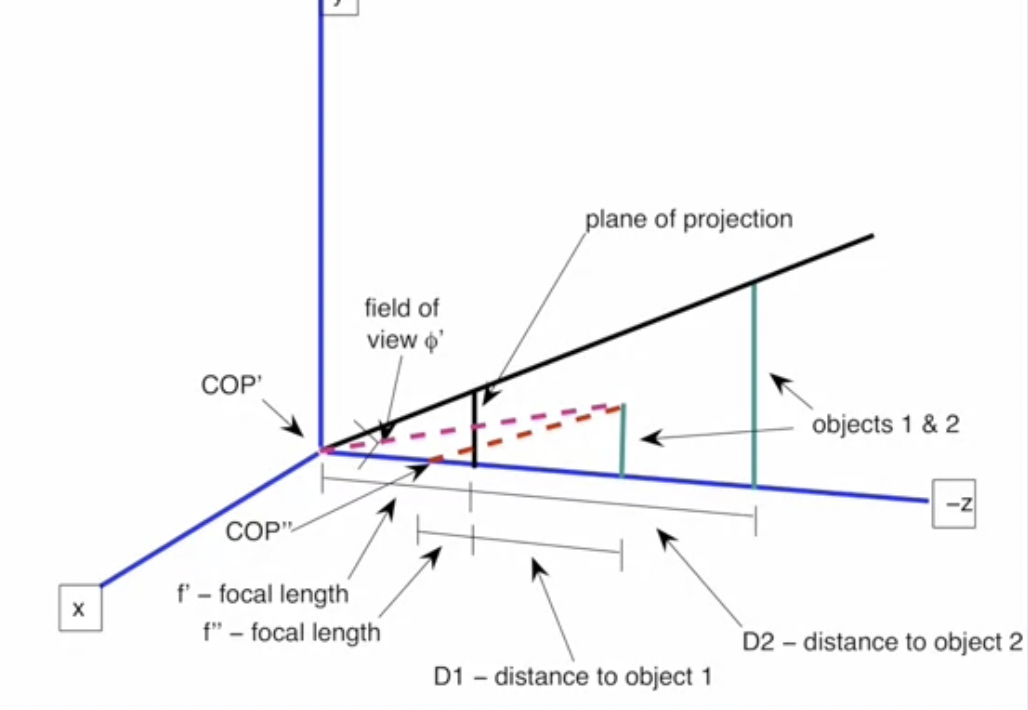
: focal length를 바꿀 때 optical center(center of projection)도 함께 이동한다
Intrinsic Camera Parameter
image plane 에서 보이는 좌표계(x', y')를 동차좌표계로 확장시키기
- 그로써 point infinity, line infinity를 쉽게 표현할 수 있게 됨
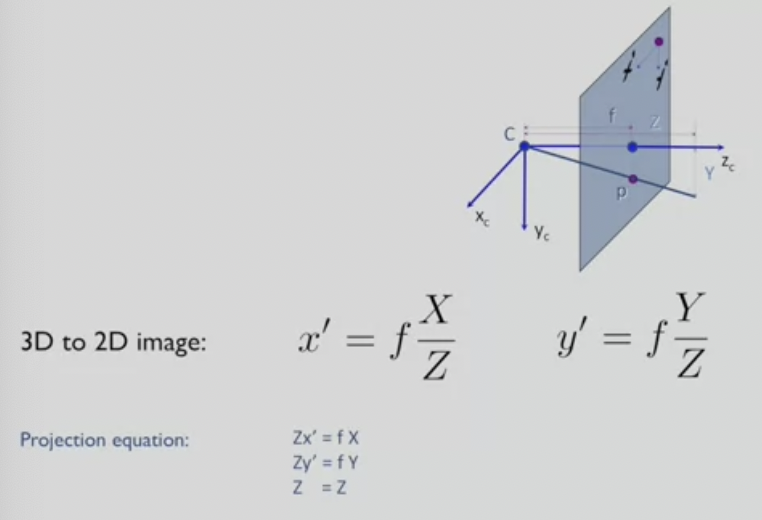
- x', y'를 가져다가 image space에서 (x', y', 1)의 동차좌표로 재표현
- 위 point를 z(camera까지의 거리)로 곱한 값 = focal length * x, y, in the 3D space
- 위 내용을 행렬곱으로 나타낼 수 있음
(step 1)
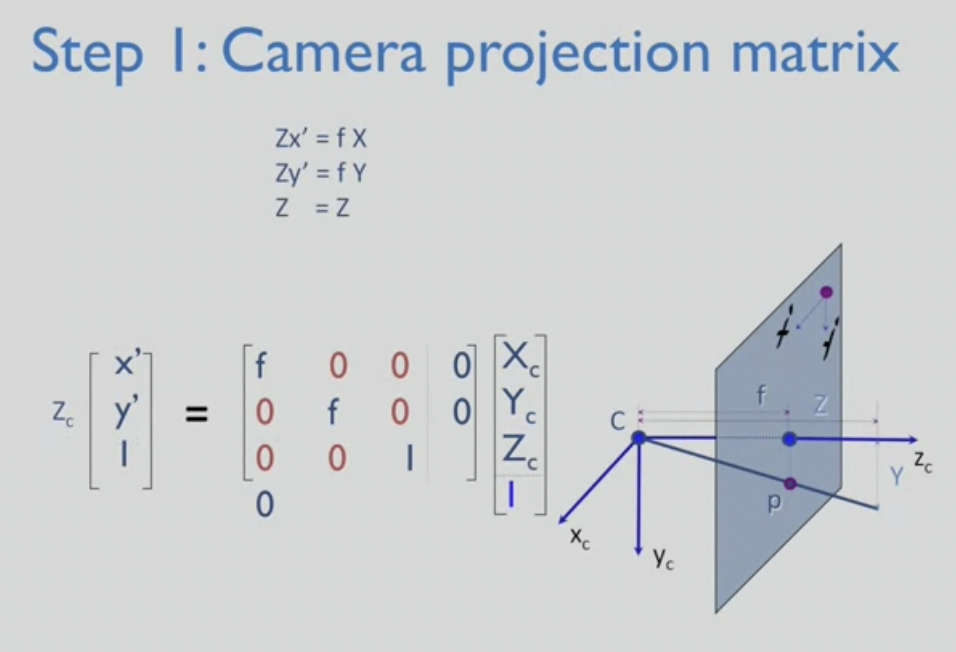
- 3D의 좌표는 (x, y, z) + 1 --> 4차원 벡터
- 3X4 크기로 된 transformation 행렬을 곱한다
- 첫 3X3은 diagoanl 형태를 띤다 : f, f, 1
- 마지막 열은 모두 0으로 되어 있음
- 2D image plane의 3차원 벡터는 2D poing (x', y', 1)의 동차좌표계에 상응한다
- image space (x', y', 1) * z 는 3D space에 ray를 형성하는데, 이 ray는 3D point들과 교차한다
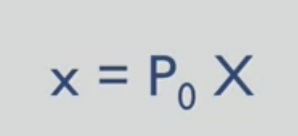
x : the image represents a point
P : camera projection matrix
X : 3D vector written down in a homogeneous coordinate in the 4D space
(step 2)
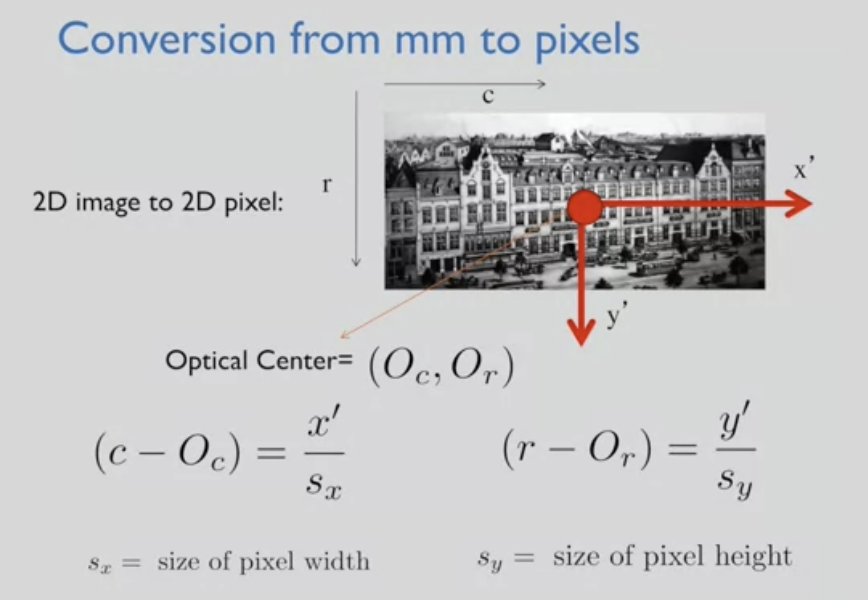
convert optical measurements (mm) to pixel coordinates (defined by matrixes)
- matrix 형태로 나타낸 이미지 : 원점 (0, 0)은 일반적으로 좌측최상단
- image plane 중앙의 optical image : 오른쪽 가리키는 x, 아래 가리키는 y
- optical world의 중심(center) = optical axis going from our eye to the image plane
--> image plane 에 수직, image plane에 닿는 point를 "principal point(주점)"라고 부름
canvas image 위 (0,0) 에서 상쇄하기
optical world에서 principal point를 왼쪽 상단으로 이동시킴 --> transformation of shift
- optical world의 측정값을 pixel의 크기로 나눔
simple linear transformation, shift from the principle point to the upper left corner followed by a scale factor
--> matrix transformation 형태로 표현
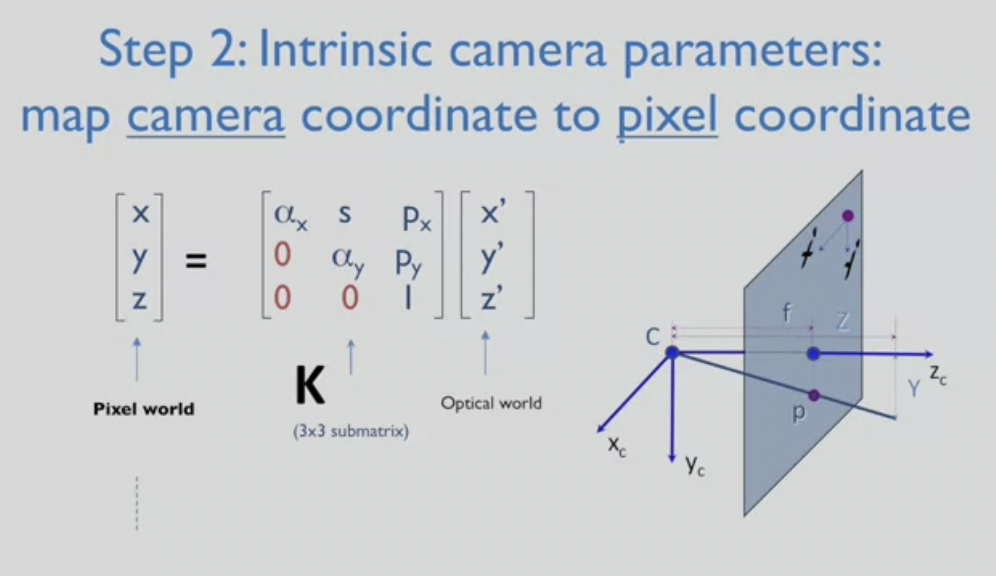
- 3x3 행렬
- ax, ay : scaling factor --> 픽셀의 크기와 관련
- px, py : principal point --> 이상적으로는 이미지 정중앙이미나 실제로는 아닐 때가 많음
- 렌즈 및 카메라 높이로 인해 image plane과 카메라가 이상적인 평행을 이루지 않을 수도 있음
--> s(slant factor) 로 표현됨
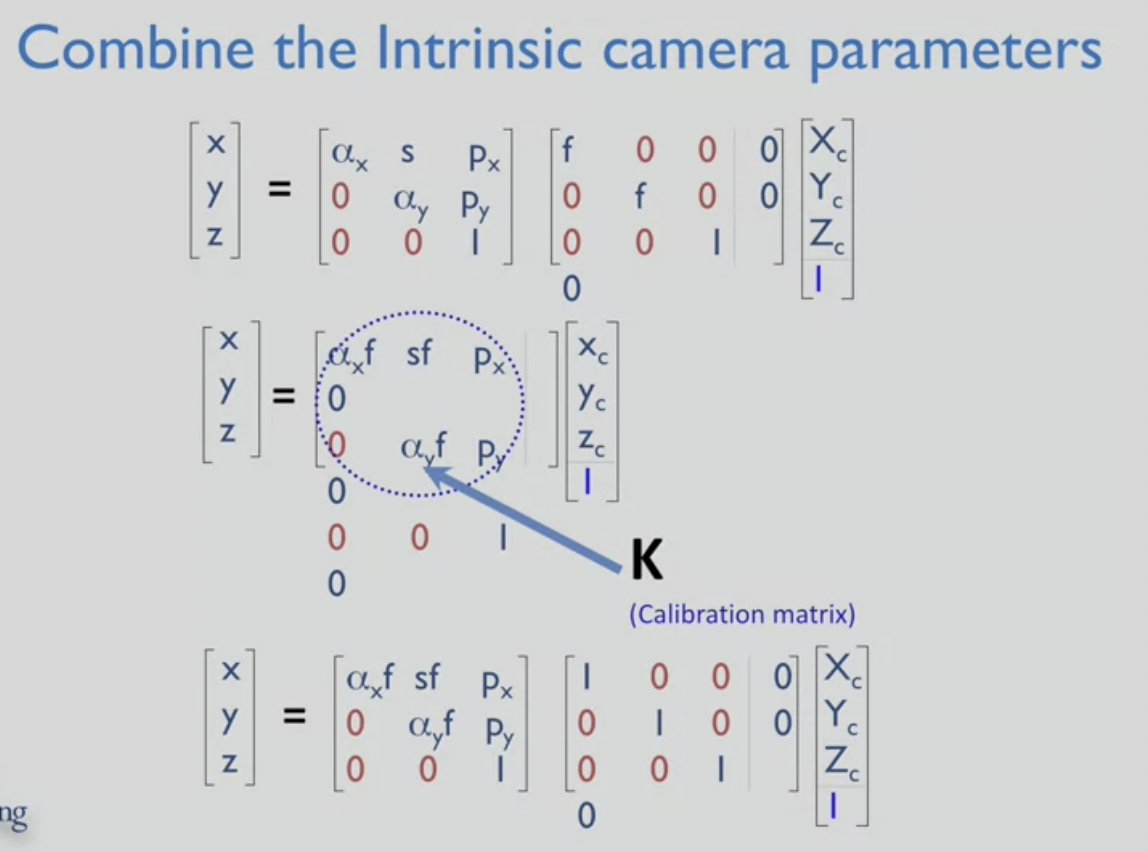
optical ray에서 pixel ray으로의 변환 + focal length = combined calibration matrix
- magnification(focal length) & magnification(pixel size)
- marix K : 3x3 으로 된 calibration matrix
[camera projection equation for 1st person camera config]
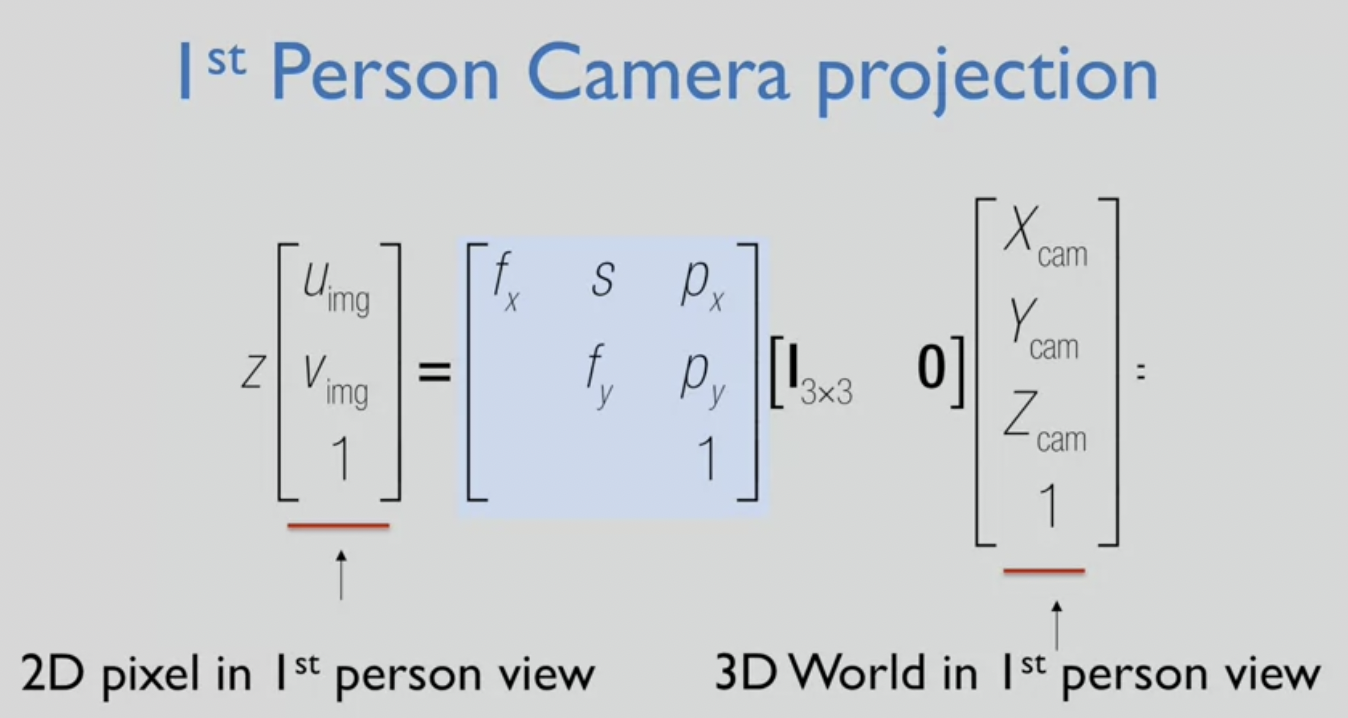
- 1st person camera view에서 측정된 3D 공간 points (내가 있는 곳이 원점, x축 오른쪽 ..)
--> 동차좌표계에서 4D 좌표 형식으로 표현됨
--> 3x3 모양 행렬로 곱하게 됨
(3D 좌표를 가져다가 3D로 내리되 ideal image plane - 2D space 에 있도록 함)
(이후 ideal image plane 이 camera calibration matrix를 활용해 pixel 도메인으로 변환)
--> 2D image이지만 동차좌표 3D ray를 표현하고 있음
- 거리 z 로 곱하면 완전히 동일하게 된다
[정리]
- 1st person camera projection matrix is a transformation of a 3D world in the 1st person measurements('나'), shrinking from a 3D space down to a 2D space
- the transformation components : camera calibration, scaling factor, principal point
--> [I 0]로 된 간단한 행렬식: 다른 reference center로 이동할수록 [I 0] 변화
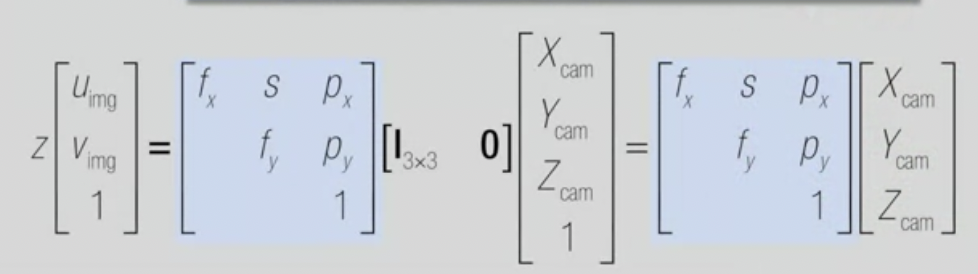
- 행렬식을 더 단순화시킬 수 있음
- XYZ 좌표의 점들을 self reference center로 가져와서, 바로 camera calibration matrix(K)로 곱한다
--> 3D ray 로 변환됨 = image plane 위 동차좌표로 표현됨
[camera calibratnio matrix K]
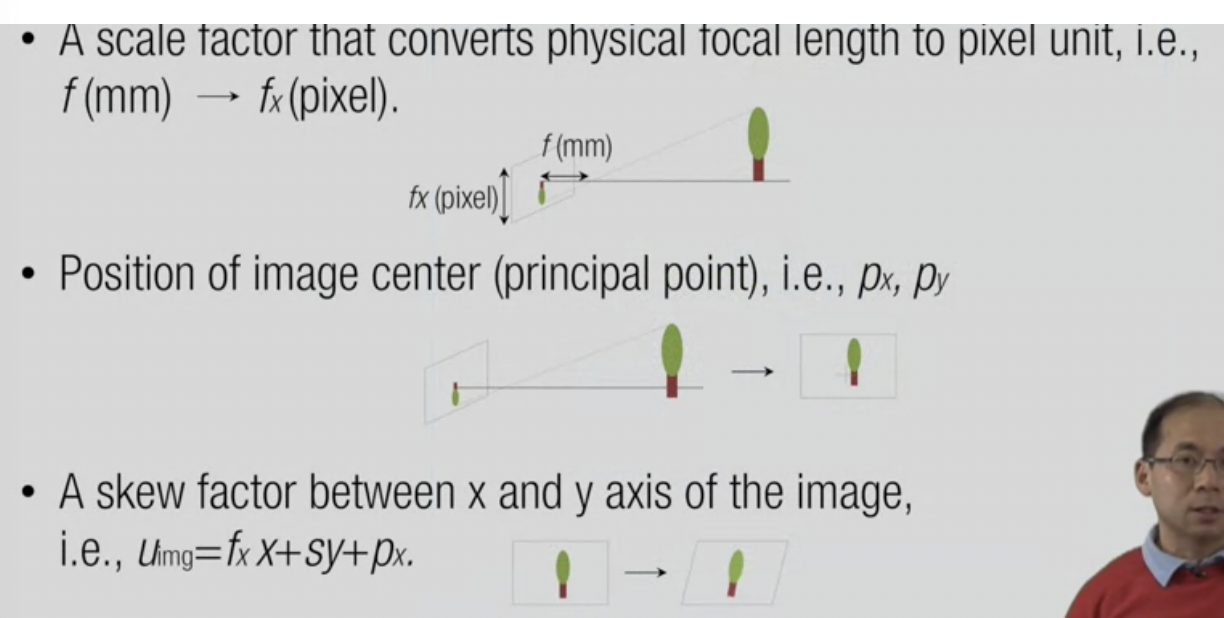
three factors
- scaling factor : focal length change &size of the pixel conversions
- optical ray : ideally image centre
- skew/slant factor : if tilted
'인공지능 > pose estimation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| How to Compute Intrinsics from Vanishing Points (0) | 2022.05.11 |
|---|---|
| 3D World to First Person Transformation (0) | 2022.05.10 |
| Rotations and Translations (0) | 2022.05.09 |
| Point-line Duality (0) | 2022.05.09 |
| Perspective Projection (0) | 2022.05.06 |